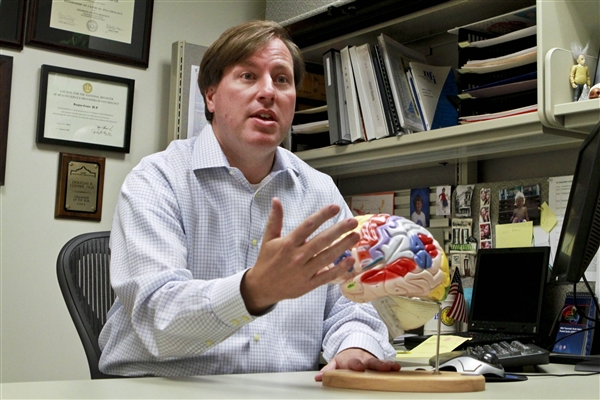
Neuro Psychologist
Apply theories and principles of neuro psychology to diagnose and treat disorders of higher cerebral functioning.
Neuro Psychologist
Neuro Psychologist
1. Apply theories and principles of neuropsychology to diagnose and treat disorders of higher cerebral functioning.
2. Conduct neuropsychological evaluations such as assessments of intelligence, academic ability, attention, concentration, sensory-motor function, language, learning, and memory.
3. Write or prepare detailed clinical neuropsychological reports using data from psychological or neuropsychological tests, self-report measures, rating scales, direct observations, or interviews.
4. Diagnose and treat conditions involving injury to the central nervous system such as cerebrovascular accidents, neoplasms, infectious or inflammatory diseases, degenerative diseases, head traumas, demyelinating diseases and various forms of dementing illnesses.
5. Interview patients to obtain comprehensive medical histories.
6. Establish neurobehavioral baseline measures for monitoring progressive cerebral disease or recovery.
7. Diagnose and treat psychiatric populations for conditions such as somatoform disorder, dementias, and psychoses.
8. Read current literature, talk with colleagues, and participate in professional organizations or conferences to keep abreast of developments in neuropsychology.
9. Diagnose and treat neural and psychological conditions in medical and surgical populations such as patients with early dementing illness or chronic pain with a neurological basis.
10. Distinguish between psychogenic and neurogenic syndromes, two or more suspected etiologies of cerebral dysfunction, or between disorders involving complex seizures.
11. Diagnose and treat pediatric populations for conditions such as learning disabilities with developmental or organic bases.
12. Provide education or counseling to individuals and families.
13. Participate in educational programs, in-service training, or workshops to remain current in methods and techniques.
14. Educate and supervise practicum students, psychology interns, or hospital staff.
15. Compare patients' progress before and after pharmacologic, surgical, or behavioral interventions.
16. Design or implement rehabilitation plans for patients with cognitive dysfunction.
Key knowledge areas
The following skills aid a Neuro psychologist carry out his/her duties with ease ;.
Psychology — Knowledge of human behavior and performance; individual differences in ability, personality, and interests; learning and motivation; psychological research methods; and the assessment and treatment of behavioral and affective disorders.
Therapy and Counseling — Knowledge of principles, methods, and procedures for diagnosis, treatment, and rehabilitation of physical and mental dysfunctions, and for career counseling and guidance.
English Language — Knowledge of the structure and content of the English language including the meaning and spelling of words, rules of composition, and grammar.
Medicine and Dentistry — Knowledge of the information and techniques needed to diagnose and treat human injuries, diseases, and deformities. This includes symptoms, treatment alternatives, drug properties and interactions, and preventive health-care measures.
Education and Training — Knowledge of principles and methods for curriculum and training design, teaching and instruction for individuals and groups, and the measurement of training effects.
Biology — Knowledge of plant and animal organisms, their tissues, cells, functions, interdependencies, and interactions with each other and the environment.
Customer and Personal Service — Knowledge of principles and processes for providing customer and personal services. This includes customer needs assessment, meeting quality standards for services, and evaluation of customer satisfaction.
Mathematics — Knowledge of arithmetic, algebra, geometry, calculus, statistics, and their applications.
Sociology and Anthropology — Knowledge of group behavior and dynamics, societal trends and influences, human migrations, ethnicity, cultures and their history and origins.
Skills
The following skills aid a Neuro psychologist carry out his/her duties with ease ;.
Reading Comprehension — Understanding written sentences and paragraphs in work related documents.
Active Listening — Giving full attention to what other people are saying, taking time to understand the points being made, asking questions as appropriate, and not interrupting at inappropriate times.
Critical Thinking — Using logic and reasoning to identify the strengths and weaknesses of alternative solutions, conclusions or approaches to problems.
Social Perceptiveness — Being aware of others' reactions and understanding why they react as they do.
Complex Problem Solving — Identifying complex problems and reviewing related information to develop and evaluate options and implement solutions.
Abilities
Deductive Reasoning — The ability to apply general rules to specific problems to produce answers that make sense.
Inductive Reasoning — The ability to combine pieces of information to form general rules or conclusions (includes finding a relationship among seemingly unrelated events).
Problem Sensitivity — The ability to tell when something is wrong or is likely to go wrong. It does not involve solving the problem, only recognizing there is a problem.
Written Comprehension — The ability to read and understand information and ideas presented in writing.
Oral Comprehension — The ability to listen to and understand information and ideas presented through spoken words and sentences.
Some of the courses that prepare students for this career
Watch and Listen what the practioneers in your field are saying