I am a
student
institution
career professional
I need help with
Career Selection & Planning
Find your best-fit career, stream, course or college through advanced assessments and expert guidance.
college applications
Get admits from your dream colleges through end-to-end applications guidance for overseas and liberal arts universities.
I am interested in
Career Development Programs
State-of-the-art career assessments, expert guidance, and more to help students plan their career paths.
Career Advancement Programs
Expert-led MUN training programs, inspirational career talks and more to help students get that added edge.
I am interested in
Getting Certified (ICCC)
Become an International Certified Career Coach through a multi-level credentialing program by Mindler & CDA (USA).
Partnering with Mindler
Expand and grow your career counselling practice by leveraging the full force of Mindler’s career guidance platform.
Ready to discover your perfect career?
Enter your email id to take the Orientation Style test for free.
CAREER COUNSELLING PROGRAMS
Class 8-9
Stream & Subject SelectionAdvanced assessment & personalised guidance to help you select the perfect stream and subjects that align you to the right careers.
Class 10-12
Career Selection & PlanningExpert guidance & 5-dimensional assessment to help you discover your perfect career and choose the right course and college.
Graduates
Career Selection & Development5-dimensional assessment & superior guidance to help you discover your perfect career and choose the best next step.
Thank you for contacting us!
One of our team members will respond in 2 working days to resolve your query. If your query is urgent, you can alternatively call our career helpline.
Ready to pave your way to your dream college?
Leave your details below and we will get in touch shortly.
COLLEGE APPLICATION PROGRAMS
Overseas Application
End-to-end overseas admissions guidance to help you build the perfect applications for your target universities.
Liberal Arts Application
Comprehensive guidance and personalised application development for admissions to Liberal Arts programs.
Thank you for contacting us!
One of our team members will respond in 2 working days to resolve your query. If your query is urgent, you can alternatively call our career helpline.
Ready to give students the best of career guidance?
Leave your details below and we will get in touch shortly.
Career Development Programs
Career Development &
Planning Ecosystem
State-of-the-art assessment & end-to-end career guidance to help students discover their perfect career.
Thank you for contacting us!
One of our team members will respond in 2 working days to resolve your query. If your query is urgent, you can alternatively call our career helpline.
Ready to give your students the added edge?
Leave your details below and we will get in touch shortly.
Career Advancement Programs
MUN Training Program
Expert-led training and comprehensive guidance sessions to help students excel at MUN conferences.
Mindler Talks
Career awareness and inspirational talks for students with professionals who have achieved success in their fields.
Thank you for contacting us!
One of our team members will respond in 2 working days to resolve your query. If your query is urgent, you can alternatively call our career helpline.
Ready to upgrade your career counselling skills?
Enter your email id to start your ICCC application.
Getting Certified (ICCC)
International Certified
Career Coach (ICCC)
A 3-month program with emphasis on global practices, experiential learning & career guidance tools.
Thank you for contacting us!
One of our team members will respond in 2 working days to resolve your query. If your query is urgent, you can alternatively call our career helpline.
Ready to grow as a counsellor?
Leave your details below and we will get in touch shortly.
Partnering with Mindler
Mindler Partner Program
World-class career assessment platform & tools to help you scale up your career counselling practice.
Thank you for contacting us!
One of our team members will respond in 2 working days to resolve your query. If your query is urgent, you can alternatively call our career helpline.
Breaking News
- Flexible Remote Work Opportunity for University Students: Earn $100–$250 Per Month ...Read More
- Ministry of Education and Sports Azerbaijan Government Scholarships For 2025-2026 Academic Year ...Read More
- Government Sponsorship Undergraduate Admission Lists 2025-26 for Makerere University ...Read More
- Ministry of Education And Sports: Egyptian Government Scholarships 2025-2026 Academic Year ...Read More
- Ground Breaker Full Scholarship for girls to study Software Engineering 2025 July Intake ...Read More
- Tony Elumelu Foundation Entrepreneurship Programme (TEEP) 2025 for young African Entrepreneurs ...Read More
- DESIGNING FUTURES 2050 International Design Competition 2025 (€15,000 prize) ...Read More
- Ground Breaker Full time Scholarship for girls to study Software Engineering 2025 Intake ...Read More
- Ministry of Education And Sports Algerian Vocational Training Scholarships for 2024-2025 AY ...Read More
- Ministry of Education and Sports Advert for the Algerian Government Scholarships for 2024-2025 ...Read More
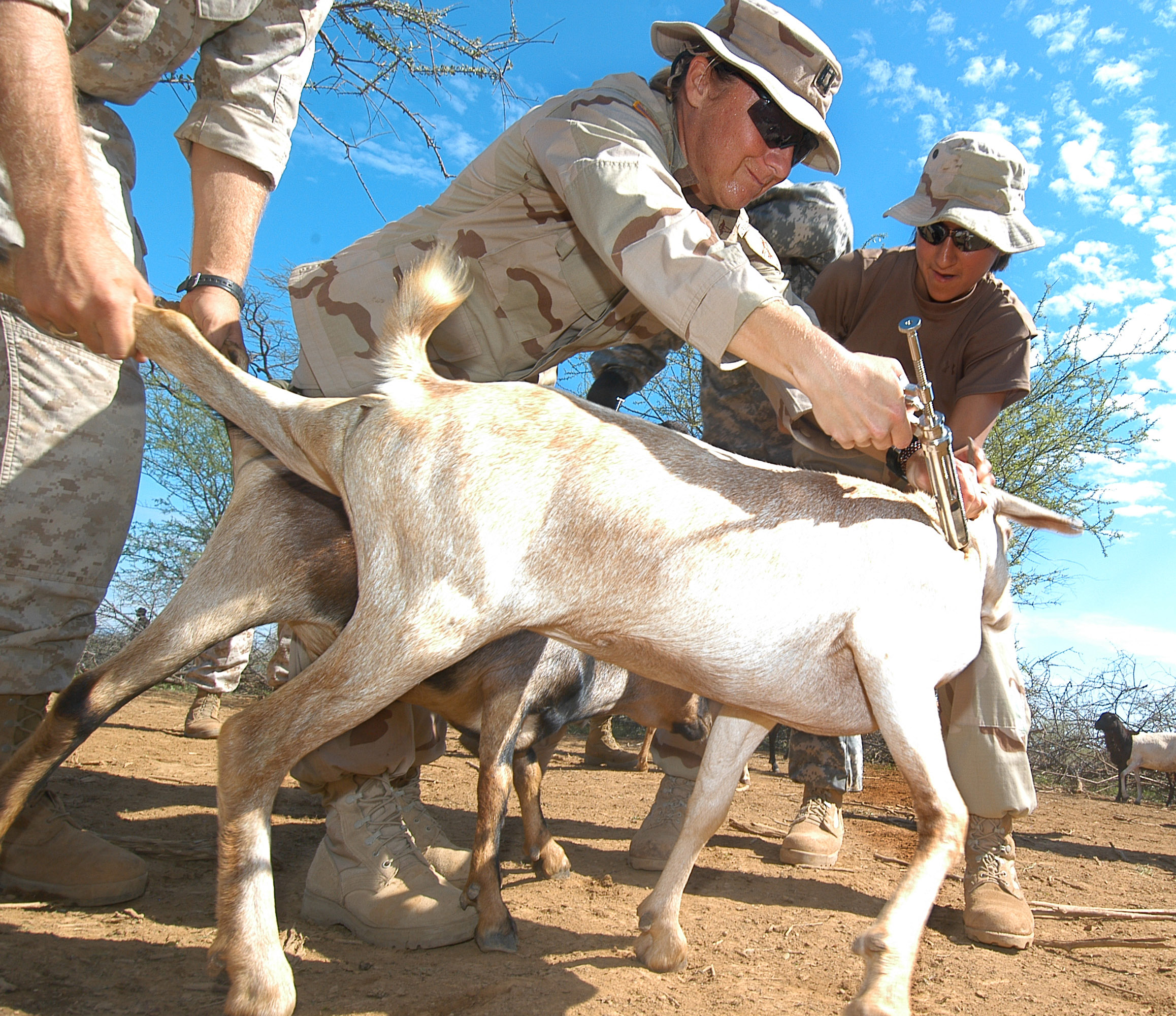
Veterinarian
Veterinarians diagnose, treat, or research illness or injuries in animals. They care for the health of animals.
Add to FavouritesA veterinary physician, colloquially called a vet, shortened from veterinarian is a professional who practices veterinary medicine by treating disease, disorder, and injury in non-human animals.
Daily tasks / Routine Activities
1. Determine protocols for medical procedures.
2. Maintain medical or professional knowledge.
3. Conduct research to increase knowledge about medical issues.
4. Immunize patients.
5. Operate on patients to treat conditions.
6. Treat acute illnesses, infections, or injuries.
7. Maintain medical facility records.
8. Analyze medical data to determine cause of death.
9. Analyze test data or images to inform diagnosis or treatment.
10. Collect biological specimens from patients.
Education
Professional degree in Veternary medicine is required for practice
Most Important Skills for Veterinarians
Reading—Reading work-related information.
Science—Using scientific rules and strategies to solve problems.
Thinking Critically—Thinking about the pros and cons of different ways to solve a problem.
Writing—Writing things for co-workers or customers.
Learning New Things—Figuring out how to use new ideas or things.
Listening—Listening to others, not interrupting, and asking good questions.
Making Decisions—Thinking about the pros and cons of different options and picking the best one.
Speaking—Talking to others.
Being Aware of Others—Understanding people's reactions.
Monitoring Performance—Keeping track of how well people and/or groups are doing in order to make improvements.
Most Important Knowledge Areas for Veterinarians
Medicine and Dentistry—Knowledge of the information and techniques needed to diagnose and treat human injuries, diseases, and deformities. This includes symptoms, treatment alternatives, drug properties and interactions, and preventive health-care measures.
Customer and Personal Service—Knowledge of principles and processes for providing customer and personal services. This includes customer needs assessment, meeting quality standards for services, and evaluation of customer satisfaction.
Biology—Knowledge of plant and animal organisms, their tissues, cells, functions, interdependencies, and interactions with each other and the environment.
English Language—Knowledge of the structure and content of the English language including the meaning and spelling of words, rules of composition, and grammar.
Chemistry—Knowledge of the chemical composition, structure, and properties of substances and of the chemical processes and transformations that they undergo. This includes uses of chemicals and their interactions, danger signs, production techniques, and disposal methods.
Sales and Marketing—Knowledge of principles and methods for showing, promoting, and selling products or services. This includes marketing strategy and tactics, product demonstration, sales techniques, and sales control systems.
Mathematics—Knowledge of arithmetic, algebra, geometry, calculus, statistics, and their applications.
Psychology—Knowledge of human behavior and performance; individual differences in ability, personality, and interests; learning and motivation; psychological research methods; and the assessment and treatment of behavioral and affective disorders.
Administration and Management—Knowledge of business and management principles involved in strategic planning, resource allocation, human resources modeling, leadership technique, production methods, and coordination of people and resources.
Computers and Electronics—Knowledge of circuit boards, processors, chips, electronic equipment, and computer hardware and software, including applications and programming.
-
 Indian Government Scholarships for 2024-2025 Academic Year
Study in India on Full Scholarship
Indian Government Scholarships for 2024-2025 Academic Year
Study in India on Full Scholarship
Know more -
Government Allied Health Training Institutions in Uganda
Licensed Government Allied Health Training Institutions
Know more -
Government Nursing and Midwifery Training Institutions offering Diploma and Certificate Programs
Licensed Government Institutions
Know more -
 Ministry of Education And Sports United Kingdom Common Wealth Scholarships 2024-2025
Masters and Phd Scholarships
Ministry of Education And Sports United Kingdom Common Wealth Scholarships 2024-2025
Masters and Phd Scholarships
Know more -
 JAB Admission to other tertiary institutions in Uganda for academic year 2023-2024 on government sponsorship
Government Sponsored students for other Tertiary Institition
JAB Admission to other tertiary institutions in Uganda for academic year 2023-2024 on government sponsorship
Government Sponsored students for other Tertiary Institition
Know more -
 Makerere University and Makerere University Business School Private Sponsorship Admission List 2023-2024
Private Sponsorship
Makerere University and Makerere University Business School Private Sponsorship Admission List 2023-2024
Private Sponsorship
Know more -
 2023 Uganda Nursing Schools Interviews For Admissions Into Certificates Programs
Suitable candidates are invited to attend ORAL interviews into CERTIFICATE programs in Health Training Institutions
2023 Uganda Nursing Schools Interviews For Admissions Into Certificates Programs
Suitable candidates are invited to attend ORAL interviews into CERTIFICATE programs in Health Training Institutions
Know more -
 Ministry of Education and Sports Algerian Government Scholarships Scheme for 2023-2024 Academic Year
Study in Algeria on Full Scholarship
Ministry of Education and Sports Algerian Government Scholarships Scheme for 2023-2024 Academic Year
Study in Algeria on Full Scholarship
Know more -
 African Palliative Care Education Scholarship Fund
Scholarship for Nurses, Social Workers, Physiotherapists
African Palliative Care Education Scholarship Fund
Scholarship for Nurses, Social Workers, Physiotherapists
Know more -
 Master of Medicine (MMed), scholarship opportunity at Mbarara University of Science and Technology
Apply for the First Mile Program
Master of Medicine (MMed), scholarship opportunity at Mbarara University of Science and Technology
Apply for the First Mile Program
Know more -
 2023-24 GSK Scholarships for Future Health Leaders
Scholarship to study a Masters at the London School of Hygiene & Tropical Medicine
2023-24 GSK Scholarships for Future Health Leaders
Scholarship to study a Masters at the London School of Hygiene & Tropical Medicine
Know more -
 DAAD Masters of Science in International Health Scholarships 2023-2024
Applications for the Masters of Science in International Health Programme at the University of Heidelberg and Charité Berlin with scholarship funding from the DAAD EPOS programme are open until 15 Oct 2022.
DAAD Masters of Science in International Health Scholarships 2023-2024
Applications for the Masters of Science in International Health Programme at the University of Heidelberg and Charité Berlin with scholarship funding from the DAAD EPOS programme are open until 15 Oct 2022.
Know more -
Ugandan Doctor Wins 2 billion shillings for research Dr Kwizera is doing the respiratory failure research
Know more -
 Commonwealth Distance Learning Scholarships 2022 at the London School of Hygiene and Tropical Medicine
Full Scholarships for Distance Learning
Commonwealth Distance Learning Scholarships 2022 at the London School of Hygiene and Tropical Medicine
Full Scholarships for Distance Learning
Know more -
 Merch Foundation Call for Application for Scholarships in Critically Underserved Specialties for Medical Graduates
Postgraduate Scholarships in the Medical Field
Merch Foundation Call for Application for Scholarships in Critically Underserved Specialties for Medical Graduates
Postgraduate Scholarships in the Medical Field
Know more -
 INTERVIEWS FOR ADMISSION INTO POST-BASIC HEALTH TRAINING INSTITUTIONS FOR ACADEMIC YEAR 2020-2021
ORAL interviews for admission into Post-Basic Health Training Institutions
INTERVIEWS FOR ADMISSION INTO POST-BASIC HEALTH TRAINING INSTITUTIONS FOR ACADEMIC YEAR 2020-2021
ORAL interviews for admission into Post-Basic Health Training Institutions
Know more -
 INTERVIEWS FOR ADMISSIONS INTO CERTIFICATE PROGRAMS IN HEALTH TRAINING INSTITUTIONS 2020-2021
ORAL interviews into CERTIFICATE programs in Health Training Institutions
INTERVIEWS FOR ADMISSIONS INTO CERTIFICATE PROGRAMS IN HEALTH TRAINING INSTITUTIONS 2020-2021
ORAL interviews into CERTIFICATE programs in Health Training Institutions
Know more -
 Commonwealth Medical Fellowships 2020 for Students in Developing Countries
The UK Department for International Development (DFID) funds the 2020 Commonwealth Medical Fellowships for mid-career medical staff from developing countries
Commonwealth Medical Fellowships 2020 for Students in Developing Countries
The UK Department for International Development (DFID) funds the 2020 Commonwealth Medical Fellowships for mid-career medical staff from developing countries
Know more -
 These 9 African healthcare startups have raised at least $1M in total venture funding
Amazing innovations in the health sciences to watch out for
These 9 African healthcare startups have raised at least $1M in total venture funding
Amazing innovations in the health sciences to watch out for
Know more -
 Makerere researchers design Ebola test
Innovations amidst adversity
Makerere researchers design Ebola test
Innovations amidst adversity
Know more -
 Ugandans invent technology that diagnoses pneumonia faster than any doctor
Necessity is the mother of Invention
Ugandans invent technology that diagnoses pneumonia faster than any doctor
Necessity is the mother of Invention
Know more -
 Meet first Ugandan pharmacist to hold patent
Innovations in Health Care
Meet first Ugandan pharmacist to hold patent
Innovations in Health Care
Know more -
 Extension of deadline of call for student loan application academic year starting 2016
Another opportunity to make it to University for your dream course
Extension of deadline of call for student loan application academic year starting 2016
Another opportunity to make it to University for your dream course
Know more -
 Mom Inspires Daughter To Be A Doctor Who Really Makes People Better
Helping HIV people cope with depression
Mom Inspires Daughter To Be A Doctor Who Really Makes People Better
Helping HIV people cope with depression
Know more
Draw Inspiration from time tested individuals
Careers that are in the same career field as Veterinarian
-
 Dentist
Know more
Dentist
Know more -
Dental Laboratory Technician Know more
-
 Pharmacist
Know more
Pharmacist
Know more -
 Veterinarian
Know more
Veterinarian
Know more -
 Surgeon
Know more
Surgeon
Know more -
 Psychiatrist
Know more
Psychiatrist
Know more -
 Health inspector
Know more
Health inspector
Know more -
 Cytotechnologist
Know more
Cytotechnologist
Know more -
 Medical laboratory technician
Know more
Medical laboratory technician
Know more -
 Nurse
Know more
Nurse
Know more -
 Physical Therapist
Know more
Physical Therapist
Know more -
 Dietitian and Nutritionist
Know more
Dietitian and Nutritionist
Know more -
 Paramedic
Know more
Paramedic
Know more -
 Health Care Social Worker
Know more
Health Care Social Worker
Know more -
 Coroner
Know more
Coroner
Know more -
 Doctor
Know more
Doctor
Know more -
 Clinical Research Coordinator
Know more
Clinical Research Coordinator
Know more -
 Medical and Health Services Manager
Know more
Medical and Health Services Manager
Know more -
 Epidemiologist
Know more
Epidemiologist
Know more -
 Chiropractor
Know more
Chiropractor
Know more -
 Dentist, General
Know more
Dentist, General
Know more -
 Oral and Maxillofacial Surgeon
Know more
Oral and Maxillofacial Surgeon
Know more -
 Orthodontist
Know more
Orthodontist
Know more -
 Prosthodontist
Know more
Prosthodontist
Know more -
 Optometrist
Know more
Optometrist
Know more -
 Pharmacist
Know more
Pharmacist
Know more -
 Anesthesiologist
Know more
Anesthesiologist
Know more -
 Family and General Practitioner
Know more
Family and General Practitioner
Know more -
 Internist, General
Know more
Internist, General
Know more -
 Obstetrician and Gynecologist
Know more
Obstetrician and Gynecologist
Know more -
 Pediatrician, General
Know more
Pediatrician, General
Know more -
 Psychiatrist
Know more
Psychiatrist
Know more -
 Dermatologist
Know more
Dermatologist
Know more -
 Hospitalist
Know more
Hospitalist
Know more -
 Neurologist
Know more
Neurologist
Know more -
 Nuclear Medicine Physician
Know more
Nuclear Medicine Physician
Know more -
 Ophthalmologist
Know more
Ophthalmologist
Know more - Pathologist Know more
-
 Physical Medicine and Rehabilitation Physician
Know more
Physical Medicine and Rehabilitation Physician
Know more -
 Preventive Medicine Physician
Know more
Preventive Medicine Physician
Know more -
 Radiologist
Know more
Radiologist
Know more -
 Sports Medicine Physician
Know more
Sports Medicine Physician
Know more -
 Urologist
Know more
Urologist
Know more -
 Physician Assistant
Know more
Physician Assistant
Know more -
 Anesthesiologist Assistant
Know more
Anesthesiologist Assistant
Know more -
 Podiatrist
Know more
Podiatrist
Know more -
 Occupational Therapist
Know more
Occupational Therapist
Know more -
 Low Vision Therapists, Orientation and Mobility Specialist, and Vision Rehabilitation Therapist
Know more
Low Vision Therapists, Orientation and Mobility Specialist, and Vision Rehabilitation Therapist
Know more -
 Physical Therapist
Know more
Physical Therapist
Know more -
 Radiation Therapist
Know more
Radiation Therapist
Know more -
 Recreational Therapist
Know more
Recreational Therapist
Know more -
 Art Therapist
Know more
Art Therapist
Know more -
 Music Therapist
Know more
Music Therapist
Know more -
 Respiratory Therapist
Know more
Respiratory Therapist
Know more -
 Speech-Language Pathologist
Know more
Speech-Language Pathologist
Know more -
 Exercise Physiologist
Know more
Exercise Physiologist
Know more -
 Registered Nurse
Know more
Registered Nurse
Know more -
 Acute Care Nurse
Know more
Acute Care Nurse
Know more -
 Advanced Practice Psychiatric Nurse
Know more
Advanced Practice Psychiatric Nurse
Know more -
 Critical Care Nurse
Know more
Critical Care Nurse
Know more -
 Clinical Nurse Specialist
Know more
Clinical Nurse Specialist
Know more -
 Nurse Anesthetist
Know more
Nurse Anesthetist
Know more -
 Nurse Midwife
Know more
Nurse Midwife
Know more -
 Nurse Practitioner
Know more
Nurse Practitioner
Know more -
 Audiologist
Know more
Audiologist
Know more -
 Acupuncturist
Know more
Acupuncturist
Know more -
 Naturopathic Physician
Know more
Naturopathic Physician
Know more -
 Orthoptist
Know more
Orthoptist
Know more -
 Medical and Clinical Laboratory Technologist
Know more
Medical and Clinical Laboratory Technologist
Know more -
 Cytogenetic Technologist
Know more
Cytogenetic Technologist
Know more -
 Cytotechnologist
Know more
Cytotechnologist
Know more -
 Histotechnologists and Histologic Technician
Know more
Histotechnologists and Histologic Technician
Know more -
 Medical and Clinical Laboratory Technician
Know more
Medical and Clinical Laboratory Technician
Know more -
 Dental Hygienist
Know more
Dental Hygienist
Know more -
 Cardiovascular Technologists and Technician
Know more
Cardiovascular Technologists and Technician
Know more -
 Diagnostic Medical Sonographer
Know more
Diagnostic Medical Sonographer
Know more -
 Nuclear Medicine Technologist
Know more
Nuclear Medicine Technologist
Know more -
 Radiologic Technologist
Know more
Radiologic Technologist
Know more -
 Emergency Medical Technicians and Paramedic
Know more
Emergency Medical Technicians and Paramedic
Know more -
 Dietetic Technician
Know more
Dietetic Technician
Know more -
 Pharmacy Technician
Know more
Pharmacy Technician
Know more -
 Psychiatric Technician
Know more
Psychiatric Technician
Know more -
 Respiratory Therapy Technician
Know more
Respiratory Therapy Technician
Know more -
 Surgical Technologist
Know more
Surgical Technologist
Know more -
 Veterinary Technologists and Technician
Know more
Veterinary Technologists and Technician
Know more -
 Ophthalmic Medical Technician
Know more
Ophthalmic Medical Technician
Know more -
 Licensed Practical and Licensed Vocational Nurse
Know more
Licensed Practical and Licensed Vocational Nurse
Know more -
 Medical Records and Health Information Technician
Know more
Medical Records and Health Information Technician
Know more -
 Optician, Dispensing
Know more
Optician, Dispensing
Know more -
 Orthotist and Prosthetist
Know more
Orthotist and Prosthetist
Know more -
 Hearing Aid Specialist
Know more
Hearing Aid Specialist
Know more -
 Neurodiagnostic Technologist
Know more
Neurodiagnostic Technologist
Know more -
 Ophthalmic Medical Technologist
Know more
Ophthalmic Medical Technologist
Know more -
 Radiologic Technician
Know more
Radiologic Technician
Know more -
 Occupational Health and Safety Technician
Know more
Occupational Health and Safety Technician
Know more -
 Athletic Trainer
Know more
Athletic Trainer
Know more -
 Genetic Counselor
Know more
Genetic Counselor
Know more -
 Midwife
Know more
Midwife
Know more -
 Home Health Aide
Know more
Home Health Aide
Know more -
 Psychiatric Aide
Know more
Psychiatric Aide
Know more -
 Nursing Assistant
Know more
Nursing Assistant
Know more -
 Orderlies
Know more
Orderlies
Know more -
 Occupational Therapy Assistant
Know more
Occupational Therapy Assistant
Know more -
 Occupational Therapy Aide
Know more
Occupational Therapy Aide
Know more -
 Physical Therapist Assistant
Know more
Physical Therapist Assistant
Know more -
 Massage Therapist
Know more
Massage Therapist
Know more -
 Dental Assistant
Know more
Dental Assistant
Know more -
 Medical Assistant
Know more
Medical Assistant
Know more -
 Medical Equipment Preparer
Know more
Medical Equipment Preparer
Know more -
 Medical Transcriptionist
Know more
Medical Transcriptionist
Know more -
 Pharmacy Assistant
Know more
Pharmacy Assistant
Know more -
 Veterinary Assistants and Laboratory Animal Caretaker
Know more
Veterinary Assistants and Laboratory Animal Caretaker
Know more -
 Phlebotomist
Know more
Phlebotomist
Know more -
 Speech-Language Pathology Assistant
Know more
Speech-Language Pathology Assistant
Know more -
 Legal Secretary
Know more
Legal Secretary
Know more -
 Magnetic Resonance Imaging Technologist
Know more
Magnetic Resonance Imaging Technologist
Know more -
 Endoscopy Technician
Know more
Endoscopy Technician
Know more -
 Cardiologist
Know more
Cardiologist
Know more -
 Radiographer
Know more
Radiographer
Know more
Online Training in Health Science
Trending Opportunities
Latest Jobs Corner
-
HR & Administration Manager NGO Jobs – Welthungerhilfe
Posted: Posted Thu, 11 Dec 2025 08:34:20 +0000 -
Fresher Dispatch/Invoicing Clerk Jobs – Jesa Farm Dairy
Posted: Posted Thu, 11 Dec 2025 08:32:24 +0000 -
Business Development Leader Jobs – Visa
Posted: Posted Thu, 11 Dec 2025 08:22:09 +0000 -
Driver Jobs – Bantwana Initiative Uganda
Posted: Posted Thu, 11 Dec 2025 08:11:49 +0000 -
Fresher Accounts Assistant Jobs – UAP Old Mutual Insurance
Posted: Posted Thu, 11 Dec 2025 08:01:33 +0000 -
Portfolio Manager – Alternative Investments Jobs – UAP Old Mutual Insurance
Posted: Posted Thu, 11 Dec 2025 07:51:18 +0000 -
Business Development Officer – Broking Jobs – UAP Old Mutual Insurance
Posted: Posted Thu, 11 Dec 2025 07:41:00 +0000 -
Program Support Specialist II – Livelihoods NGO Jobs – Compassion International
Posted: Posted Thu, 11 Dec 2025 07:30:40 +0000 -
Several No Experience Graduate Engineer – Electrical Jobs – Gachey Group
Posted: Posted Thu, 11 Dec 2025 07:20:28 +0000 -
Head of Legal & Regulatory Affairs Jobs – Gachey Group
Posted: Posted Thu, 11 Dec 2025 07:10:17 +0000
Advertisement
Trending Opportunities
Advertisement
Popular Careers
-
Civil Engineer
30173 Views -
Actor
24363 Views -
Flight attendant
22367 Views -
Fashion Designer
20621 Views -
Pilot and flight engineer
19261 Views