Breaking News
- Flexible Remote Work Opportunity for University Students: Earn $100–$250 Per Month ...Read More
- Ministry of Education and Sports Azerbaijan Government Scholarships For 2025-2026 Academic Year ...Read More
- Government Sponsorship Undergraduate Admission Lists 2025-26 for Makerere University ...Read More
- Ministry of Education And Sports: Egyptian Government Scholarships 2025-2026 Academic Year ...Read More
- Ground Breaker Full Scholarship for girls to study Software Engineering 2025 July Intake ...Read More
- Tony Elumelu Foundation Entrepreneurship Programme (TEEP) 2025 for young African Entrepreneurs ...Read More
- DESIGNING FUTURES 2050 International Design Competition 2025 (€15,000 prize) ...Read More
- Ground Breaker Full time Scholarship for girls to study Software Engineering 2025 Intake ...Read More
- Ministry of Education And Sports Algerian Vocational Training Scholarships for 2024-2025 AY ...Read More
- Ministry of Education and Sports Advert for the Algerian Government Scholarships for 2024-2025 ...Read More
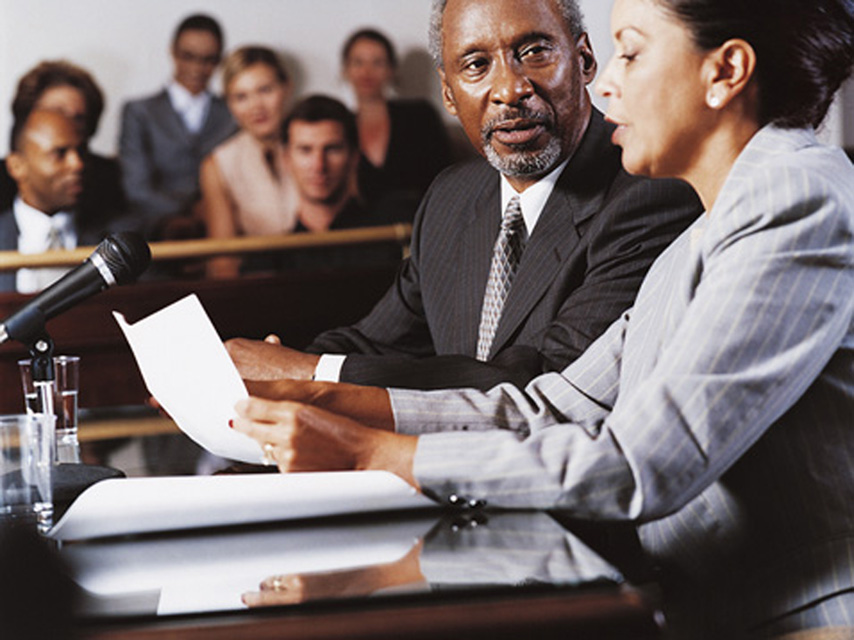
Paralegal
Assist lawyers by investigating facts, preparing legal documents, or researching legal precedent. Conduct research to support a legal proceeding, to formulate a defense, or to initiate legal action.
Add to FavouritesA paralegal is an individual, qualified by education, training or work experience who is employed or retained by a lawyer, law office, corporation, governmental agency or other entity and who performs specifically delegated substantive legal work for which a lawyer is responsible.
Tasks
1. Prepare affidavits or other documents, such as legal correspondence, and organize and maintain documents in paper or electronic filing system.
2. Prepare for trial by performing tasks such as organizing exhibits.
3. Prepare legal documents, including briefs, pleadings, appeals, wills, contracts, and real estate closing statements.
4. Meet with clients and other professionals to discuss details of case.
5. File pleadings with court clerk.
6. Gather and analyze research data, such as statutes, decisions, and legal articles, codes, and documents.
7. Call upon witnesses to testify at hearing.
8. Investigate facts and law of cases and search pertinent sources, such as public records, to determine causes of action and to prepare cases.
9. Direct and coordinate law office activity, including delivery of subpoenas.
10. Keep and monitor legal volumes to ensure that law library is up-to-date.
11. Appraise and inventory real and personal property for estate planning.
12. Arbitrate disputes between parties and assist in the real estate closing process, such as by reviewing title searches.
Key knowledge areas
1. English Language — Knowledge of the structure and content of the English language including the meaning and spelling of words, rules of composition, and grammar.
2. Law and Government — Knowledge of laws, legal codes, court procedures, precedents, government regulations, executive orders, agency rules, and the democratic political process.
3. Clerical — Knowledge of administrative and clerical procedures and systems such as word processing, managing files and records, stenography and transcription, designing forms, and other office procedures and terminology.
4. Computers and Electronics — Knowledge of circuit boards, processors, chips, electronic equipment, and computer hardware and software, including applications and programming.
5. Customer and Personal Service — Knowledge of principles and processes for providing customer and personal services. This includes customer needs assessment, meeting quality standards for services, and evaluation of customer satisfaction.
Skills
Reading Comprehension — Understanding written sentences and paragraphs in work related documents.
Active Listening — Giving full attention to what other people are saying, taking time to understand the points being made, asking questions as appropriate, and not interrupting at inappropriate times.
Speaking — Talking to others to convey information effectively.
Writing — Communicating effectively in writing as appropriate for the needs of the audience.
Critical Thinking — Using logic and reasoning to identify the strengths and weaknesses of alternative solutions, conclusions or approaches to problems.
Time Management — Managing one's own time and the time of others.
Active Learning — Understanding the implications of new information for both current and future problem-solving and decision-making.
Coordination — Adjusting actions in relation to others' actions.
Judgment
Decision Making — Considering the relative costs and benefits of potential actions to choose the most appropriate one.
Monitoring — Monitoring/Assessing performance of yourself, other individuals, or organizations to make improvements or take corrective action.
Service Orientation — Actively looking for ways to help people.